Fiscalization 2.0
Documentation Menu
Newsletter Subscription
Fiscalization 2.0
e-Invoice
What is an eInvoice and why do you need it?
An eInvoice, or electronic invoice, is an invoice that is issued, sent, and received in a structured electronic format. This format allows for automatic processing without paper or manual data entry. Folowing the implementation of the Fiscalization Act from January 1, 2026, all taxpayers registered in the VAT register with their headquarters, residence, or habitual abode in the Republic of Croatia will be required to send and receive eInvoices for domestic transactions.
Tax Authority is responsible for Fiscalization 2.0. More information can be found on its official website https://porezna.gov.hr/fiskalizacija/bezgotovinski-racuni.
We suggest to watch our webinar with the full details of the scoope of the Fiscalization law (currently only in croatian) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=89uvg8bgfWI
How to prepare?
1. Link your list of goods and services with the Classification of Products by Activity of the Republic of Croatia, 2025.
- Taxpayers subject to the Fiscalization Act will be required to link each item of goods and services in the eInvoice with the correct classification code and display it in the eInvoice as a six-digit numeric code.
- For the purposes of the Fiscalization Act, the valid statistical standard Classification of Products by Activity – CPA is used.
- Searching the CPA 2025 is available via the KLASUS application on the website of the Croatian Bureau of Statistics.
- For assistance in applying the classification, the email KPD@dzs.hr is available.
- In the ‘Documentation’ section, an illustrated guide for searching classification codes is available.
2. Choose an information intermediary
- An information intermediary is a legal or natural person that enables you to create, send, and receive eInvoices with other business entities.
- A list of authorized information intermediaries will be available on the Tax Administration’s Fiscalization portal (this list will be updated after September 1, 2025, as intermediaries receive certificates of compliance).
- Choose the intermediary that suits you best (check prices and service offerings).
3. Sign a contract with the information intermediary
- After selecting and contracting an intermediary, you will gain access to their system through which you can create and exchange eInvoices.
- It is possible to arrange for them to immediately handle the fiscalization of exchanged incoming and outgoing eInvoices on your behalf.
4. Authorize the information intermediary in the Fiscalization and eReporting Application (FiskApplication)
- Through the FiskApplication, you must confirm that the contracted intermediary may receive eInvoices on your behalf and assign authorization to whoever will perform fiscalization.
5. Start using eInvoice exchange systems
Once everything is set up, you can start using the intermediary’s solution for creating, sending, and receiving eInvoices, as well as for fiscalization. This significantly automates business operations, speeds up processes, and saves resources – with proper preparation, the eInvoice can be an opportunity to modernize your business model.
Each exchanged eInvoice can be downloaded and delivered to your accountant, unless your accountant is already integrated with the intermediary – in which case, everything is handled automatically.
By December 31, 2025, eInvoice recipients must provide and confirm their address for locating the final receiving address of eInvoices via the Metadata Services Directory (AMS).
Submitting data to AMS can be done:
- independently, if you have your own metadata service, or
- through a metadata service provider, who will submit the data to AMS on your behalf.
To ensure timely preparation for upcoming business changes, the Tax Administration continuously publishes documents available in the ‘Documentation’ section. Please note that documents are periodically updated to adapt to the development of IT solutions for secure and accurate eInvoice exchange.
Classification of goods and services in eInvoices
Selected questions on the classification of products by activity
In the eInvoice/Documentation section, selected questions on the classification of products by activity (CPA) are published.
About the Classification of Products by Activity of the Republic of Croatia, 2025 (CPA 2025)
CPA 2025 is the central product classification and statistical standard used for the collection and publication of product-level data and for international data exchange. It is fully aligned with the Statistical Classification of Products by Activity – CPA 2.2 of the European Union.
You can find more information regarding KPD classification codes in document that Croatian Tax Authority published on a web site from of Tax Authority .
(UPDATE 2025-12-03) Diagram of F 2.0 from ERP & MER standpoint
Donwload diagram below which describes all steps in exchanges of the invoices, fiscalization and eReporting.
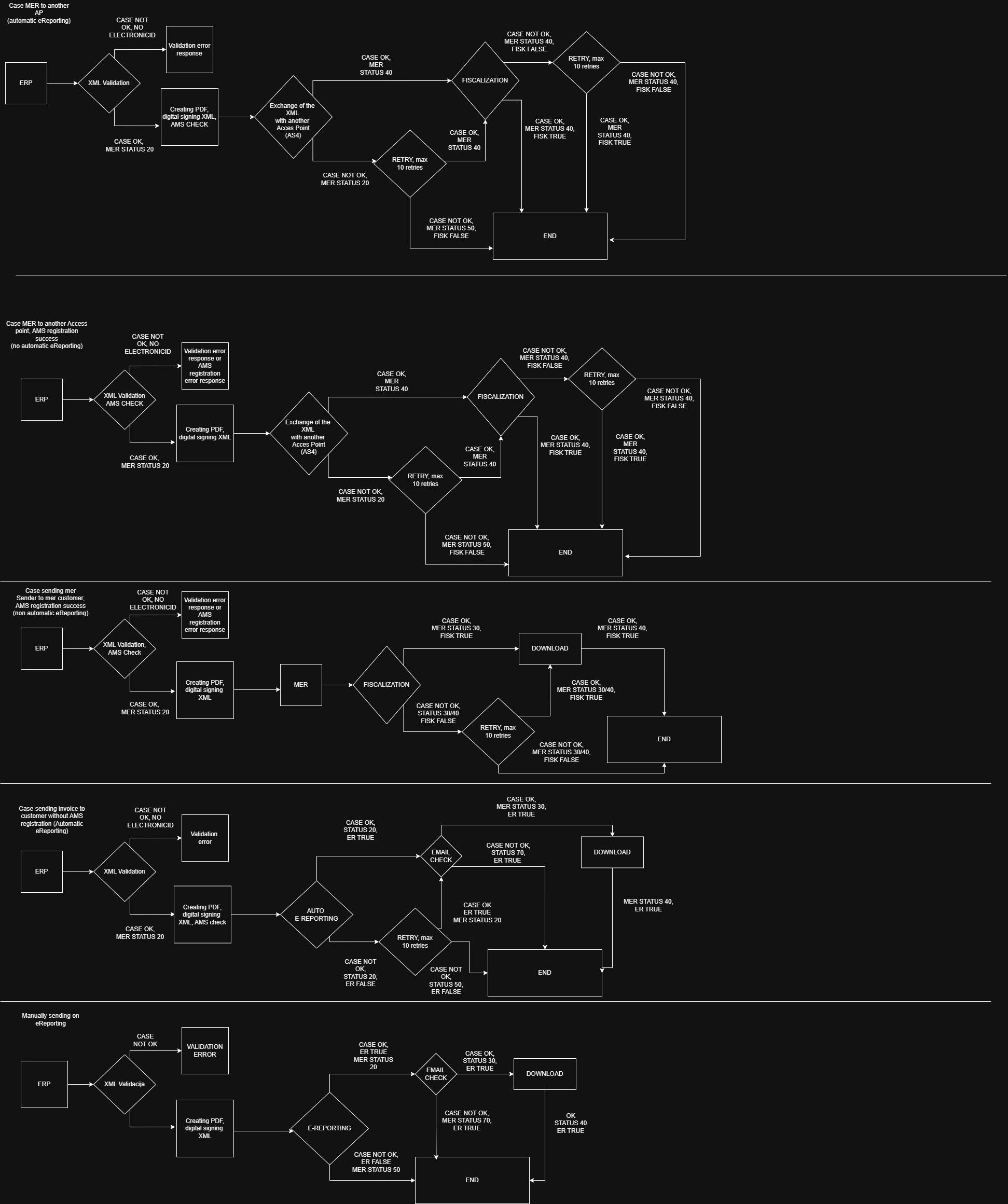
Flow of eInvoice exchange between ERP system of a supplier through MER to the customer:
Step 1.
Supplier creates XML of the eInvoice inside ERP system. ERP sends XML to MER system
Step 2. (UPDATE 2025-12-03)
MER receives XML for processing.
Step 2.a
MER will validate XML before sending it to fiscalization system or eReporting. If XML fails on validation, MER rejects document from futher processing.
Step 2.b.
MER system pings AMS and checks if the customer is registered in AMS. Based on the answer from AMS, MER initiate sending document to another Access point or rejects document from further processing.
NOTE: New feature is automatic eReporting for mer senders. In that case, mer will not reject document in case customer is not registered in AMS, rather it will generate request and send document to eReporting automatically.
In case XML and AMS registration is OK, MER will send eDocument to the Access point of the customer and then it will do the fiscalization of sent document.
Step 3.
Supplier ERP system pulls status of the fiscalization or eReporting if previous step is succesfully executed
Step 3.a.
ERP pulls status of the sent eInvoice periodically (to get information in case customer rejected eInvoice).
Step 3.b.
In case fiscalization or eReporting failed, mer will retry to do the fiscalization or eReporting 10 times in next 5 days.
After 5 days of retrying, mer will update status of fiscalization or eReporting to false (Neuspješno) and sender will have to resubmit document to mer (updated XML in case there was an issue with XML).
Step 4.
Supplier sends payment information via ERP system to MER who sends it to TaxAuthority system in case fiscalization was successful.
